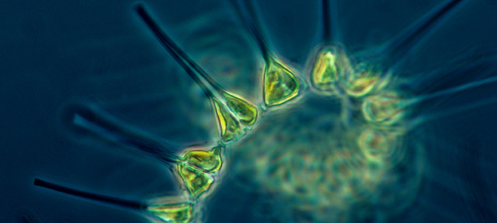
Also called algae...
Phytoplankton are organisms in the lake water that conduct photosynthesis. These organisms are typically (but not always) microscopic and they form the base of most lake foodwebs. The terms "phytoplankton" and "algae" are often used interchangeably, although phytoplankton also includes photosynthetic bacteria, which are technically not algae.
Like terrestrial plants, algae are photosynthetic, that is they use the energy of the sun to convert carbon dioxide into sugar. Oxygen is a biproduct of photosynthesis. Therefore, algae are critical to oxygen production in lakes. Algae vary in size and may only be a single cell visible under a microscope or may be multicellular and visible to the human eye (such as kelp). Algae are abundant on Earth as they come in many different forms and different species exist in freshwater and marine environments and are likely to exist in both terrestrial and aquatic environments wherever light touches. Although most commonly found or noticed in aquatic environments, algae can grow on walls, trees, and soils and may even form symbiotic relationships with animals and fungi. Algae can survive depths of up to 250 m in marine environments and may even be found in hot springs and lava flows!
Like terrestrial plants, algae are photosynthetic, that is they use the energy of the sun to convert carbon dioxide into sugar. Oxygen is a biproduct of photosynthesis. Therefore, algae are critical to oxygen production in lakes. Algae vary in size and may only be a single cell visible under a microscope or may be multicellular and visible to the human eye (such as kelp). Algae are abundant on Earth as they come in many different forms and different species exist in freshwater and marine environments and are likely to exist in both terrestrial and aquatic environments wherever light touches. Although most commonly found or noticed in aquatic environments, algae can grow on walls, trees, and soils and may even form symbiotic relationships with animals and fungi. Algae can survive depths of up to 250 m in marine environments and may even be found in hot springs and lava flows!
Top left image of phytoplankton by NOAA at: https://oceanservice.noaa.gov/facts/phyto.html
Top right image of pond scum from Kentucky State at: https://www.johnson.k-state.edu/images/Algae%201.jpg
Bottom left image of a kelp forest taken by NOAA and found at: https://oceanservice.noaa.gov/facts/kelp.html
Bottom right is a micrograph of blue-green algae taken by B.R. Speer and found at: https://www.e-education.psu.edu/egee439/node/693
Top right image of pond scum from Kentucky State at: https://www.johnson.k-state.edu/images/Algae%201.jpg
Bottom left image of a kelp forest taken by NOAA and found at: https://oceanservice.noaa.gov/facts/kelp.html
Bottom right is a micrograph of blue-green algae taken by B.R. Speer and found at: https://www.e-education.psu.edu/egee439/node/693
Algae Characteristics and Ecological Importance
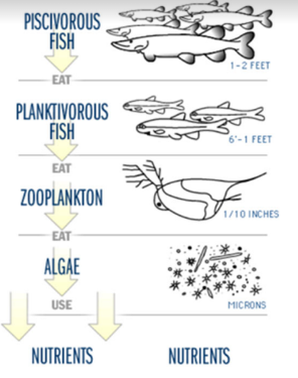 Image from lakeaccess.org
Image from lakeaccess.org
Algae are autotrophic, meaning they derive energy from the sun using photosynthesis and store this energy in carbohydrates like glucose. Most algae have a pigment called chlorophyll that aids in the process of photosynthesis. This is the pigment that makes algae (and terrestrial plants) look green. During photosynthesis, algae use carbon dioxide and produce oxygen. Therefore, algae play a critical role in providing oxygen for fish and other lake organisms. The carbohydrates produced as a product of photosynthesis are stored in the algae and fuel organisms higher up the food chain like larval fish and amphibians, zooplankton, insects, and even some waterfowl!
Some things that make algae different from plants are:
Some things that make algae different from plants are:
- Algae do not have roots
- Algae lack leaves
- Algae do not have vascular systems
Location |
|