What is a watershed?
A watershed is an area of land that contains a common set of streams and rivers that all drains into a single larger body of water such as a larger river, lake, or ocean. This area is also referred to as a catchment.
Why are watersheds important?
Aquatic environments are linked to their watersheds. Lakes are particularly sensitive to activities within their watersheds. The geology, soil, vegetation, and even the animals within the watershed impact the structure and function of the lake ecosystem.
Surface and subsurface runoff from the watershed provides the lake with carbon, nutrients, and other materials.
Landuse within watersheds can have drastic impacts on lake ecosystems. Extensive agriculture can increase nutrient inputs to the lake. Development that converts soils to impervious surfaces can result in increased runoff and shoreline erosion. Winter road treatments can lead to salinization of lakes.
Surface and subsurface runoff from the watershed provides the lake with carbon, nutrients, and other materials.
Landuse within watersheds can have drastic impacts on lake ecosystems. Extensive agriculture can increase nutrient inputs to the lake. Development that converts soils to impervious surfaces can result in increased runoff and shoreline erosion. Winter road treatments can lead to salinization of lakes.
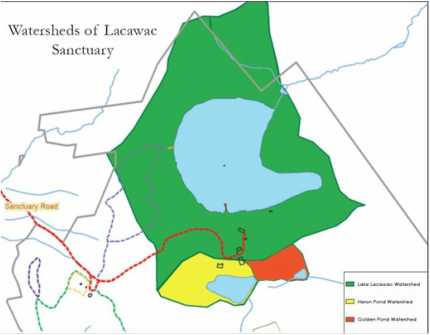
The three watersheds here are Lake Lacawac Watershed, Heron Pond Watershed, and Golden Pond Watershed.
Location |
|